Important Things Every New Convert Muslim Should Know

- Hidayah
- Network
- | Role: Hidayah Network

As you embrace Islam, understanding fundamental aspects can greatly enhance your spiritual growth. Islam is home to amazing concepts that are bound to change your life. Today, we will guide you thoroughly about what you should learn and practice after you’ve converted to a Muslim. We are sure that our expert guidance will make following and practicing Islam easier for you.
You must understand the differences between Halal and Haram. Learn about the five pillars of Islam, such as Salah, Zakat, Fast, Hajj, etc. In addition, learn about the basic Fiqh rules, you must also have basic knowledge of Seerah. And most importantly, you must avoid shirk of all kinds. Learn all of these things by enrolling yoursef in online islamc course under the supervision of qualified Islamic tutors.
Table of Contents
Toggle10 Things That Every New Convert Muslim Should Know
Keeping all that in mind, let’s begin our journey on this path of righteousness and explore the wonderful world of Islam that will bring you ever so closer to Allah (SWT).
1. Differences Between Halal and Haram
Understanding the distinctions between Halal and Haram is crucial for a newly converted Muslim, as it forms the basis of ethical and lawful living in Islam. This knowledge guides daily choices, ensuring adherence to Islamic principles.
Below is a table summarizing key aspects of Halal and Haram:
| Halal (Permissible) | Haram (Forbidden) |
| Halal food and beverages | Consumption of pork and its products |
| Salah (prayer) and acts of worship | Involvement in usury (Riba) |
| Charity (Zakat) and helping others | Consumption of intoxicants (alcohol, drugs) |
| Honest and ethical business practices | Engaging in gambling or games of chance |
| Modesty in dress (Hijab for women) | Unlawful relationships or premarital sex |
| Seeking knowledge and education | Dishonesty, lying, and false testimony |
| Respect for parents and family values | Backbiting or gossiping about others |
| Marriage and family life within Islamic guidelines | Engaging in fraud or theft |
| Ethical behavior and good manners (Adab) | Participation in activities harmful to health |
| Environmental stewardship | Associating partners with Allah (Shirk) |
Get 40% OFF Now!
2. Learning About the 5 Pillars of Islam

For a newly converted Muslim, comprehending the 5 Pillars of Islam is pivotal as they embody the core principles and practices. These pillars serve as a comprehensive guide, shaping a believer’s spiritual journey, fostering a deep connection with Allah, and establishing the foundation for a purposeful Islamic life.
Five Pillars of Islam
1. Shahada
- Offering: Professing the oneness of Allah and the prophethood of Muhammad (SAWW).
- Importance: Forms the basis of the Islamic faith, declaring a commitment to monotheism.
2. Salah
- Offering: Performing five daily prayers facing the Kaaba.
- Importance: Strengthens the connection with Allah, fostering discipline and mindfulness.
3. Zakat
- Offering: Giving a portion of wealth to the less fortunate.
- Importance: Promotes social justice, empathy, and shared responsibility for the community’s welfare.
4. Fasting
- Offering: Abstaining from food, drink, and sinful behavior during daylight hours in Ramadan.
- Importance: Develop self-discipline, empathy for the needy, and spiritual purification.
5. Hajj
- Offering: Undertaking a pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a lifetime, if possible.
- Importance: Fosters unity among Muslims, symbolizing equality, humility, and submission to Allah’s will.
3. The Significance of the 6th Pillar of Iman
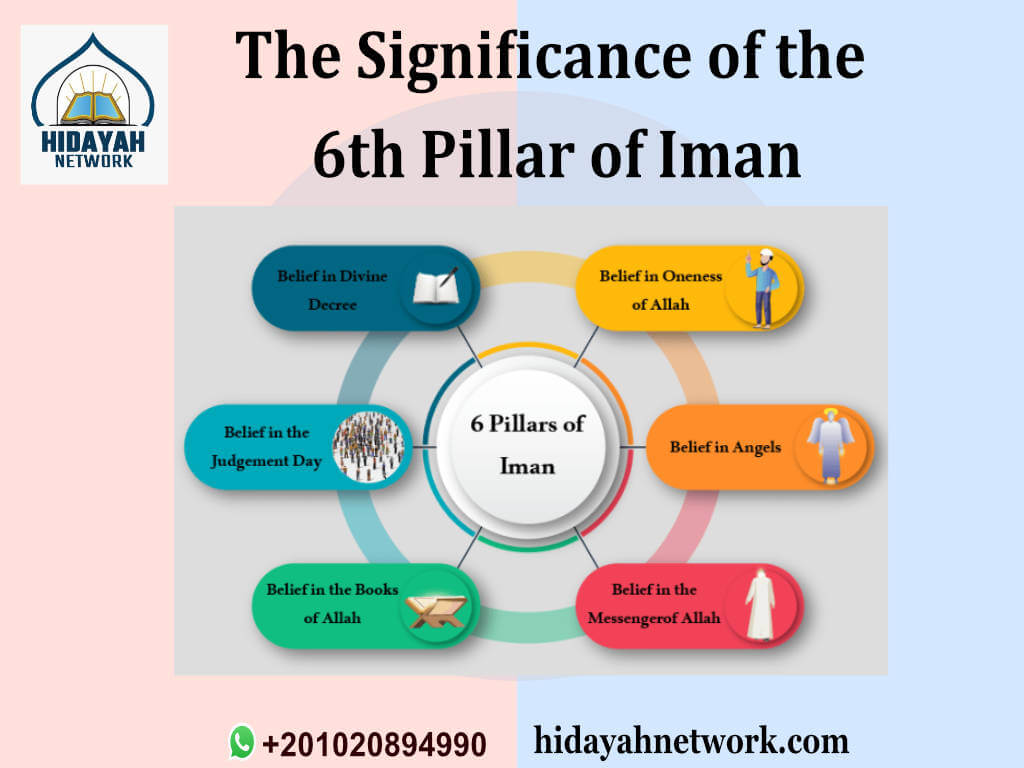
The belief in the Day of Judgment constitutes the 6th Pillar of Iman (faith) in Islam, holding profound significance for believers. Described extensively in the Quran, the concept encapsulates a day when all souls will be resurrected for divine judgment. If we Muslims get to know the importance of seeking Islamic knowledge in Islam and practicing it in real life can make our lives easy in this world as well as on the day of judgment.
As mentioned in Surah Al-Zalzalah (99:6-8), “So whoever does an atom’s weight of good will see it, and whoever does an atom’s weight of evil will see it.” This underscores the meticulous accountability for every action.
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) elucidated further in Sahih Bukhari (Hadith 6494), stating, “The people will be resurrected (and judged) according to their intentions.” This Hadith emphasizes the scrutiny of intentions, highlighting the importance of sincere actions.
4. Understanding Basic Fiqh Rules
For a newly converted Muslim, grasping basic Fiqh rules is essential as they provide practical guidance on daily life in alignment with Islamic principles.
Fiqh offers clarity on permissible (halal) and forbidden (haram) actions, shaping a believer’s conduct and ensuring adherence to Islamic law.
- Purity in Worship: Ritual purification before Salah.
- Prayer Times: Observing the prescribed timings for Salah.
- Legal Transactions: Ensuring fairness and honesty in business dealings.
- Dietary Laws: Adhering to Halal food and avoiding Haram substances.
- Social Ethics: Respecting parents, neighbors, and practicing honesty.
- Family Matters: Adhering to Islamic guidelines in marriage and divorce.
- Judicial Matters: Seeking justice and fairness in legal disputes.
5. Islamic Ethics in Daily Life
Embracing Islamic ethics in daily life is crucial for a newly converted Muslim as it shapes character, relationships, and conduct. Quranic guidance and Hadith offer timeless wisdom, serving as a moral compass for righteous living.
Surah Al-Ma’idah (5:8): “And do not let the hatred of a people prevent you from being just.”
Surah Al-Hujurat (49:13): “O mankind, indeed We have created you from male and female and made you peoples and tribes that you may know one another.”
Narrated by Anas bin Malik (Hadith 6011): “None of you will have faith till he wishes for his (Muslim) brother what he likes for himself.”
6. Basic Knowledge of Seerah
Grasping the basics of Seerah (Prophet Muhammad’s biography) is vital for a newly converted Muslim as it provides insight into the exemplary life to emulate. It serves as a source of inspiration, guidance, and understanding of the Prophet’s role in Islam.
- Surah Al-Ahzab (33:21): “Indeed, in the Messenger of Allah, you have an excellent example.”
- Surah Al-Qalam (68:4): “And indeed, you (Muhammad) are of a great moral character.”
7. Learning to Read Surah Fatiha and Other Short Surahs

For a newly converted Muslim, learning to recite Surah Fatiha and other short surahs is crucial for effective prayer and a deeper connection with Allah. These verses hold profound meanings and reciting them enriches spiritual engagement.
Short Surahs for Memorization
- Surah Al-Ikhlas (112)
- Surah Al-Falaq (113)
- Surah An-Nas (114)
- Surah Al-Kawthar (108)
- Surah Al-Mulk (67)
- Surah Ar-Rahman (55)
- Surah Al-Asr (103)
- Surah Al-Fatiha (1)
8. Avoiding Shirk of All Kinds
Understanding and avoiding all forms of Shirk (associating partners with Allah) is paramount for newly converted Muslims. This knowledge safeguards the pure monotheistic foundation of Islam, ensuring sincere worship and unwavering faith. Surah Al-Baqarah (2:21): “O mankind, worship your Lord, who created you and those before you, that you may become righteous.”
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) stressed the significance of avoiding Shirk. During the conquest of Mecca, he recited Surah Al-Nasr (110) as a proclamation of divine victory, emphasizing the pure worship of Allah over any form of associating partners.
9. Know Most Important Basic Hadiths
Grasping foundational Hadiths is pivotal. These sayings of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) provide practical guidance, moral lessons, and a deeper understanding of Islam, shaping the believer’s conduct and faith.
1. Hadith on Intentions (Niyyah)
Sahih Bukhari (1) “Actions are judged by intentions.”
2. Hadith on Kindness to Parents
Reference: Sahih Bukhari (5971) “Paradise lies at the feet of your mother.”
3. Hadith on the Importance of Knowledge
Reference: Sunan Ibn Majah (1/1/33) Explanation: “Seeking knowledge is obligatory for every Muslim.”
4. Hadith on Truthfulness
Reference: Sahih Muslim (2607) “Truth leads to righteousness, and righteousness leads to Paradise.”
5. Hadith on Mercy and Compassion
Reference: Sahih Bukhari (6013) “Those who show mercy will be shown mercy by the Most Merciful.”
10. Duties Towards Everyone in the Society
Islam emphasizes a comprehensive set of duties towards everyone in society, cultivating compassion, and fostering a sense of community. The Quran (Al-Baqarah 2:83) underscores the obligation to show kindness to parents, relatives, orphans, and the needy.
The Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) emphasized in Sahih Muslim (32) that “none of you has faith until he loves for his brother what he loves for himself,” emphasizing the universality of compassion.
The Quran further guides in Surah Al-Hujurat (49:13), “O mankind, indeed We have created you from male and female and made you peoples and tribes that you may know one another.” This encourages harmonious relations beyond familial ties, promoting unity and understanding. Top of Form
Conclusion
Islam teaches us to spread love, kindness, and respect to everyone in our society. From family to neighbors, and beyond, our duties extend to all.
The Quran and Prophet Muhammad’s (PBUH) teachings guide us, emphasizing compassion and unity. Let’s remember the beautiful saying: “None of you truly believes until you wish for others what you wish for yourself.”

About Author
